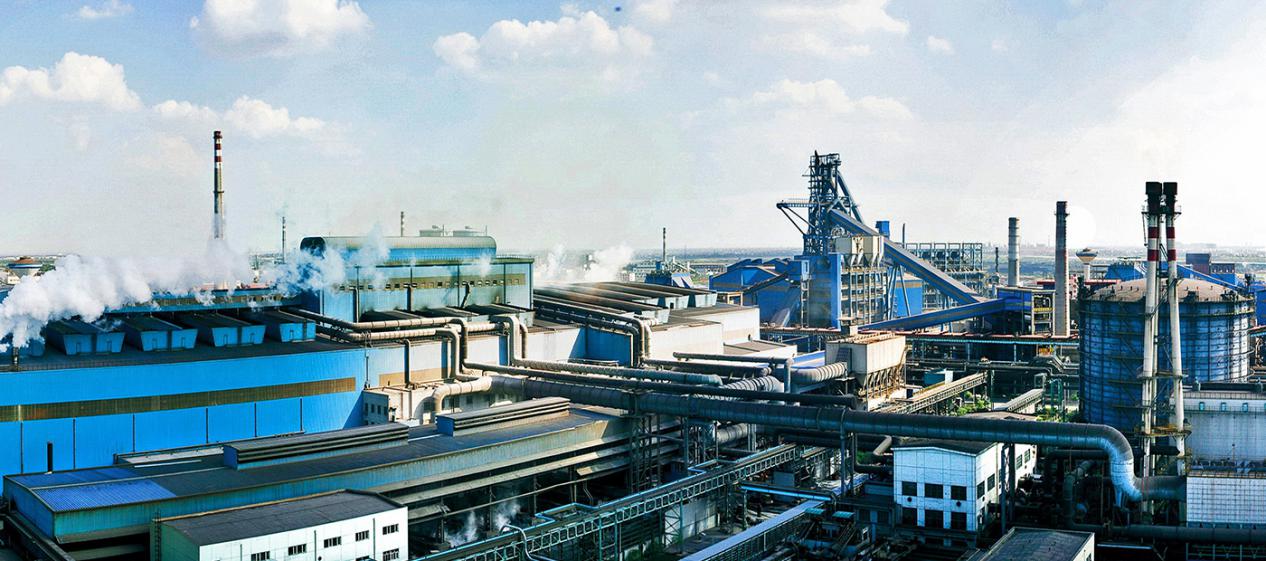
1, according to the quality of classification
(1) ordinary steel (P 0.045% or less, S 0.050% or less)
(2) the high quality steel (P, S are 0.035% or less)
(3) the high quality steel (P 0.035% or less, S 0.030% or less)
2, the classified by chemical composition
Mild steel (1) carbon steel: a. 0.25% or less (C); B. medium carbon steel (C acuities were 0.25 ~ 0.60%); C. high carbon steel (0.60%) or less c.
(2) alloy steel: a. low alloy steel (alloy element content of total 5% or less); B. in alloy steel (alloy element total content > 5 ~ 10%); C. high alloy steel (alloy element total content > 10%).
3, according to the forming method of classification
(1) forging steel; (2) cast steel; (3) hot rolled steel, (4) cold-drawn steel.
4, according to the microstructure classification
(1) annealing state: a. hypoeutectoid steel (ferrite + pearlite); B. eutectoid steel (pearlite); C. hypereutectoid steel (pearlite and cementite); D. ledeburite steel (pearlite and cementite).
(2) is the state of the fire: a. pearlitic steel; B. bainite steel; C. martensitic steel; D. austenitic steel.
(3) without phase change or part of a phase change
5, according to the classification purpose
(1) construction and engineering steel: a. ordinary carbon structural steel; B. low alloy structural steel; C. reinforced steel.
(2) structural steel: a. machinery manufacturing quenched and tempered steel: (a) structural steel; (b) surface hardening steel: including carburizing steel, permeability of ammonia steel, surface quenching steel; (c) free cutting steel; (d) cold plastic forming steel: including cold-formed steel, cold heading steel.
B. spring steel
C. bearing steel
(3) tool steel: a. carbon tool steel; B. alloy tool steel; C. high speed tool steels.
(4) the special performance of steel: a. acid-proof stainless steel; B. heat resistant steel, including oxidation heat intensity steel, steel, steel valve; C. electrothermal alloy steel; D. wear resistant steel; E. cryogenic steel; F. electrical steel.
(5) professional steel, such as Bridges with steel, ship steel, boiler steel, pressure vessel steel, agricultural machinery, steel, etc.
6, comprehensive classification
(1) ordinary steel
A. Q195 carbon structural steel: (a); (b) Q215 (A, b); (c) Q235 (A, B, c); (d) Q255 (A, B); Q275 (e).
B. low alloy structural steel
C. special-purpose common structural steel
(2) the high quality steel (including high quality steel)
A. high quality carbon structural steel structural steel: (a); (b) alloy structural steel; (c) spring steel; (d) free cutting steel; (e) bearing steel; (f) specific USES high quality steel.
B. tool steel carbon tool steel: (a); (b) alloy tool steel, (c) high speed tool steels.
Post time: Jun-03-2021